In today's digital age, the way we view content has dramatically transformed, and at the forefront of this evolution is the versatile LED display. Dive into our comprehensive guide to uncover the intricacies of LED display technology, from its rich history and working mechanism to its diverse applications and undeniable advantages. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or just curious about the screens that surround us, this article promises a deep dive into the glowing world of LED displays, illuminating their significance in our modern landscape.

What is an LED Display?
LED display is composed of LED dots electronic display screen, through the red and green light beads to replace the screen display content forms such as text, animation, pictures and video of the timely conversion, through the modular structure of the component display control. Mainly divided into Display module is the LED light array constitutes the screen luminous. Control system is to regulate the light in the region to control system is to regulate the light in the region to achieve the content of the screen display conversion. power supply system is the input voltage and current conversion to meet the needs of the display screen to meet the needs of the display screen. LED screen can be realized on a variety of information presented in different forms of mode of transformation, and LED screen can be realized on a variety of information presented in different forms of mode of transformation, and indoor and outdoor can be used, with other display screen incomparable advantages.
LED Display Performance Characteristics
-
High-intensity luminescence. In the refraction of sunlight, the screen surface content can be high definition in the visual range.
-
High level of grayscale control, LED display can be used 1024 ~ 4096 level of grayscale control clearly and realistically show more than 16.7M colors to ensure that the picture super three-dimensional sense.
-
High driving power. The scanning method is based on static latching to guarantee high-intensity bright light.
-
In order to ensure the best playback effect, LED display in different background environments can be adjusted through the automatic function to reasonably control the light.
-
Circuit integration mainly with the help of large-scale imported devices to enhance the reliability of operation, which is conducive to maintenance and debugging work. and debugging work.
-
Using modern digital processing technology to deal with video. The main choice of scanning technology distribution, design and presentation of modular, static constant-current drive, automatic adjustment of the light, and thus achieve the effect of high fidelity of the picture, the front side of the no ghosting, and improve the clarity of the image picture.
-
A wide variety of information displays, such as icons, video, text, animation, pictures, etc.
Types of LED Displays
The world of LED displays is diverse, catering to various needs from tiny device indicators to colossal billboards. Let's delve into the primary types of LED displays that have marked their presence in the technological landscape:
Direct-view LED Displays
These displays use individual LED units as pixels. By emitting red, green, and blue light, these pixels represent the full spectrum of visible colors. You'll primarily find these in large outdoor displays like digital billboards, stadium screens, and some high-end indoor screens.
Backlit LED Displays
A fusion of LED and LCD technology, these displays use LEDs for backlighting.
-
Edge-lit LED: By positioning LEDs around the screen's edges, this design offers a slimmer profile perfect for sleek TV sets and computer monitors.
-
Full-array LED: With LEDs set behind the entire display, some advanced versions offer localized dimming, enhancing contrast. These are reserved for high-end TVs prioritizing picture quality.
SMD Display
SMD refers to a type of LED module where the individual red, green, and blue LEDs are mounted onto a single surface or substrate. This configuration allows for closer packing of the LEDs, resulting in higher resolution displays with better color consistency and viewing angles. It's worth noting that advancements in LED technology have led to the development of even more compact SMD LEDs, further pushing the boundaries of display resolution and clarity.
OLED
Revolutionizing display technology, OLEDs employ organic compounds for each pixel to emit its own light, eliminating the need for backlighting. From premium TVs to modern smartphones, OLEDs are favored for their deep blacks, rapid response times, and potential for ultra-thin designs.
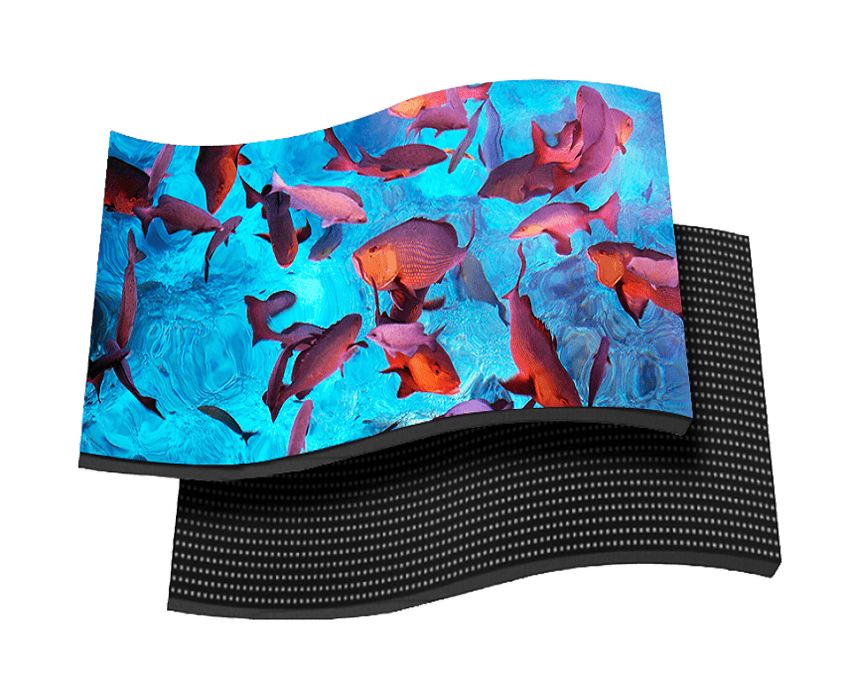
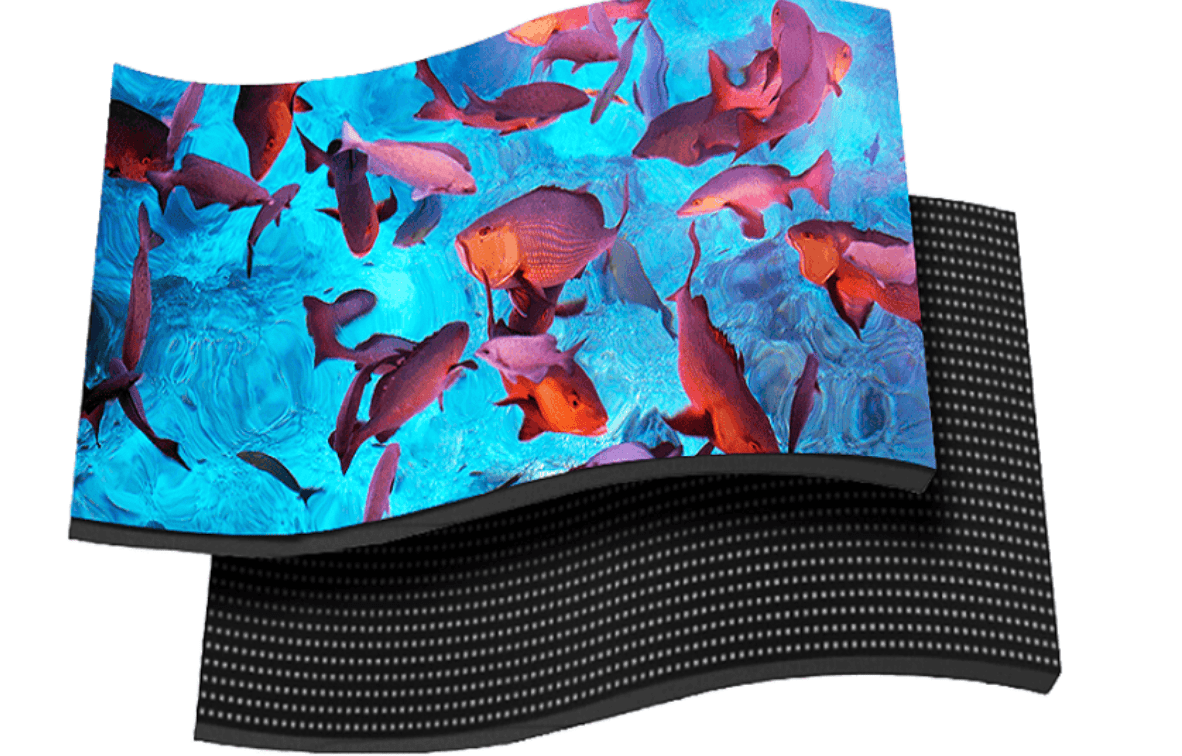
Flexible and Foldable LED Displays
Typically derived from OLED technology, these displays can bend, fold, or roll without breaking. The tech industry buzzes with foldable smartphones and wearables using these displays, promising a future where screens adapt to our needs, not the other way around. Learn more about our flexible led display.

Transparent LED Displays
Transparent LEDs are used to make the panel see-through, allowing viewers to see both the displayed content and the background. Imagine seeing both the display content and the world behind it. That's the magic of transparent LEDs. Learn more about our transparent led display.
MicroLED
An exciting entrant, MicroLEDs are incredibly tiny LEDs forming individual, self-emissive pixels. Touted as the next big thing, MicroLEDs are eyed for next-gen TVs, monitors, and even smart glasses.
Applications of LED Displays
LED displays have firmly cemented their position as a preferred medium in various sectors due to their unparalleled brightness, efficiency, and clarity. Let's dive into the diverse applications of LED displays:
1. Consumer Electronics
-
Smartphones and Tablets: Modern mobile devices often utilize LED-backlit screens for their bright visuals and energy efficiency.
-
Television Sets: From OLED to QLED, LED technology has revolutionized TV displays, offering viewers more vibrant colors and deeper blacks.
2. Advertising & Public Signage
-
Billboards: Digital LED billboards provide dynamic advertising, allowing for content changes in real-time and night-time visibility.
-
Information Boards: Airports, train stations, and bus terminals utilize LED displays to present travel schedules, alerts, and advertisements.
3. Retail and Businesses
-
Digital Signage: Stores and malls showcase product information, promotions, and branding content on LED screens.
-
Transparent LED Displays: Retail storefronts are embracing transparent LED technology to merge digital marketing while allowing visibility into the store.
4. Healthcare
-
Medical Monitors: High-definition LED screens in medical equipment provide accurate visuals, crucial for patient diagnosis and monitoring.
5. Transportation
-
Vehicle Displays: From car dashboards to infotainment systems, LEDs make the driving experience more vibrant and informative.
-
Traffic Signals: LED traffic lights are more energy-efficient and have a quicker response time than traditional bulbs.
6. Entertainment and Sports
-
Stadium Screens: Massive LED screens in stadiums relay live action, ensuring spectators don't miss a moment.
-
Concerts and Events: Dynamic stage backgrounds, tickers, and visual effects are made possible with LED panels.
7. Work and Education
-
Computer Monitors: Office workstations and home computers benefit from LED screens' clarity and reduced eye strain.
-
Interactive Boards: Educational institutions use LED-backed interactive boards for interactive teaching and presentations.
8. Industrial
-
Control Rooms: Industries with control rooms, such as power plants and traffic control centers, use LED displays for real-time monitoring and operations.
9. Architectural and Design
-
Building Facades: Architectural designs incorporate LED panels to create interactive and aesthetic building exteriors.
-
Interior Design: LED screens aren't just functional; they're also becoming a design element in modern homes and offices.
10. Wearable Technology
-
Smartwatches and Fitness Bands: These devices feature small LED displays to show time, notifications, and health metrics.
Advantages of LED Over Traditional Displays
1. The full-color display equipped with high-quality LED tube core, which makes the screen imaging high-definition, color uniformity and low power consumption. In the meantime, the screen body is lightweight and the screen layer is thin, wide-area viewing angle, so its failure rate is small and is easy maintenance.
2. The main use of a multimedia display card PCTV card with a variety of functions, the reality of the performance is more excellent. More advanced capture methods can accurately capture the video, and the Studio editing software to match the display card.
3. DVI interface technology is more advanced. Without the use of A/D and D/A conversion to ensure the integrity of the screen image, reduce the details of the possibility of fully reproducing the computer image on the display screen. DVI can support all display modes, which ensures smooth and reliable data display at the same time with a variety of integrated functions.
4. Using indoor full-color system to alleviate the system display transmission of a large number of complex data hidden problems, full true color reproduction. Using the chip to complete the data distribution display task, the received data for pulse output conversion, from 8-bit (8bit) display data to 12-bit PWM conversion, upgraded to 4096 (12bit) level of grayscale control, to achieve the screen display of non-linear 256 levels of visual grayscale, and to fully create a full-fledged color visual enjoyment.
5. Driving mode adopts a constant current system. Through its highly cost-effective, perfect LED tube voltage drop discrete insufficient to overcome the mosaic problem, to ensure that the picture texture.
6. Combine the modes of fiber optic transmission to reduce signal loss in transmission.
How to Choose the Right Led Display
LED displays are an increasingly popular choice for both commercial and personal use, known for their energy efficiency and bright, clear images. Whether you’re contemplating an LED display for advertising, entertainment, or informative purposes, understanding your options is essential. Here are top tips to guide your LED display selection:
1. Understand the Core Technology:
-
Basic Understanding: At its core, an LED (Light Emitting Diode) display comprises tiny diodes that light up when electricity flows through them. This principle, when replicated thousands or millions of times over a panel, creates the vibrant displays we use today.
-
LED vs. OLED: While both are LED-based, OLED (Organic LED) displays use organic compounds that emit light when electricity is applied. OLEDs can provide deeper blacks and can be more flexible, but might not be as long-lasting in some scenarios.
2. Determining Purpose and Placement
-
Outdoor Advertising: Think billboard-sized, high-brightness, wide-viewing angles. They should be visible even in direct sunlight.
-
Indoor Displays: These may be used for exhibitions, presentations, or events. Here, color accuracy, resolution, and clarity take precedence.
3. Outdoor vs. Indoor
-
Weather Resistance: Outdoor displays need protection from rain, dust, and direct sunlight. They should also be resistant to UV rays to prevent color fading.
-
Temperature Tolerance: Outdoor screens must handle cold winters and hot summers without malfunctioning.
-
Brightness and Resolution: Indoor displays often have higher resolutions and don't need the extreme brightness of outdoor screens.
4. Resolution Essentials:
-
Pixel Pitch: This is the distance between individual LEDs. Smaller pitches (like 1mm or 2mm) are ideal for close-up viewing, while larger pitches are suitable for screens viewed from a distance.
-
Resolution Metrics: The terms Full HD, 4K, and 8K refer to the number of pixels on the screen. Higher pixel counts mean sharper images and videos.
5. Brightness and Contrast:
-
Nits and Lumens: Brightness for displays is measured in nits. For context, indoor displays might range from 200 to 500 nits, while outdoor displays can go over 2000 nits.
-
Contrast Ratios: This denotes the difference between the brightest and darkest parts of the image. Higher ratios mean deeper blacks and more vivid images.
6. Connectivity Options:
-
Modern Inputs: Ensure support for HDMI, DVI, and DisplayPort. Depending on the application, you might also need SDI or even older connectors like VGA.
-
Wireless and Networked Options: Some displays can connect via Wi-Fi or Ethernet for centralized content management.
7. Color Depth and Calibration
-
Bit Depth: A display's bit depth refers to the number of colors it can produce. A higher bit depth (like 10-bit or 12-bit) can show billions of colors.
-
Calibration Tools: Over time, colors can drift. Calibration ensures consistent color representation over the display's lifespan.
8. Durability and Maintenance
-
Lifespan: A good LED display can last upwards of 100,000 hours. Consider brands known for longevity.
-
Module Replacement: Individual LED modules should be easy to replace if they malfunction.
Conclusion
In our rapidly evolving digital age, LED displays have firmly established themselves as a pivotal technology, driving advancements in visual communication and entertainment. From understanding the intricate mechanism behind LED technology to dissecting the diverse types of LED displays available, it's evident that these screens offer unparalleled brightness, energy efficiency, and adaptability. With applications spanning from commercial advertising billboards to intricate indoor setups, their versatility is undeniable. Moreover, with the surge in fine pixel pitch SMD displays, clarity and resolution have reached unprecedented heights. As we continue to embrace the digital era, LED displays will undoubtedly remain at the forefront, shaping our visual experiences and setting new standards for the future.
As seasoned suppliers of LED displays, we're here to illuminate your path. If you have any questions or require guidance on the best display solution for your needs, don't hesitate to reach out. Your visual aspirations are our command. Contact us today and let's brighten your vision!